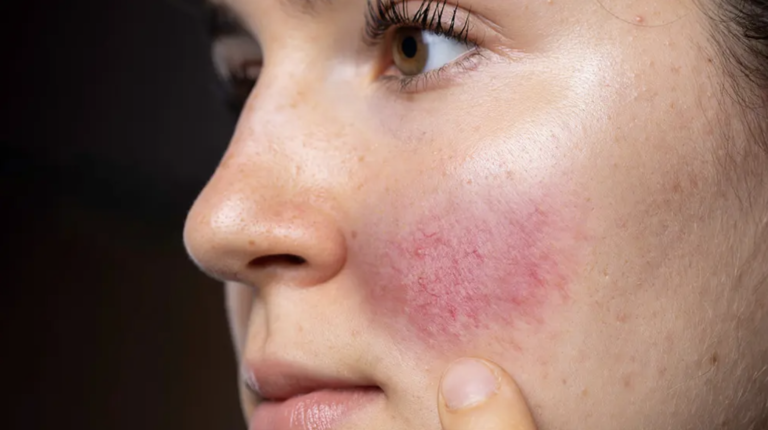
Rosacea is an inflammatory skin condition. Factors such as obesity, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to its development. The most common form—erythematotelangiectatic rosacea—is widely known as couperose. It’s essential to understand what should be avoided and what can be used in managing the condition.
We discussed this with Dr. Sara Pruneddu, our dermatologist.
What causes rosacea?
The exact causes of rosacea are still unknown, but several contributing factors have been identified:
- Genetic predisposition: Individuals with a family history of rosacea are more likely to develop the condition.
- Innate immune system dysfunction: An abnormal production of cathelicidin, a protein that fights bacteria but can also trigger inflammation and activate immune responses.
- Microorganism overgrowth: Inflammatory reactions can also be triggered by an increased presence of microorganisms normally found on the skin. Among them, the most studied is the Demodex folliculorum, a mite that lives in hair follicles.
- Ultraviolet (UV) radiation: Sun exposure can worsen rosacea by stimulating the release of vasoactive substances and free radicals, both of which promote inflammation.
- Excessive vasodilation: The release of various substances in response to different stimuli can lead to excessive blood vessel dilation.
Recommendations
What to avoid:
Managing rosacea requires avoiding triggers of facial flushing or flare-ups, such as:
- Sun exposure
- Intense physical activity
- Sudden temperature changes
- Psychological stress
- Alcohol consumption
- Spicy foods
- Harsh cosmetic products
- Creams or ointments with corticosteroids
Avoid using astringents, toners, and exfoliants, as they can irritate sensitive skin. Instead, opt for gentle cleansers and daily application of emollient creams specifically designed for rosacea-prone skin.
Importantly, corticosteroid creams should be avoided, as they may offer temporary relief but often cause rebound flare-ups when discontinued.
Can rosacea be treated naturally?
Rosacea is a chronic condition, so while it cannot be completely cured, several natural approaches can help reduce symptoms:
- Avoid direct heat sources on the face
- Minimize UV exposure
- Limit intake of hot or spicy foods and drinks
- Reduce or eliminate alcohol consumption
Daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreens is highly recommended.
Can I get rid of rosacea marks? Is there a specific cream?
There are several prescription topical treatments available, including:
- Azelaic acid
- Metronidazole
- Ivermectin
These have been shown to reduce inflammation and visible symptoms effectively. However, rosacea can resemble other skin conditions, so it’s essential to consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
